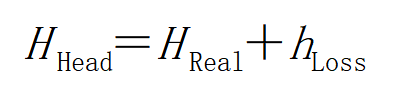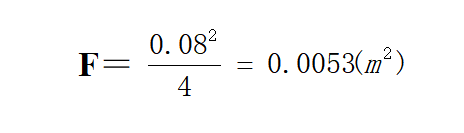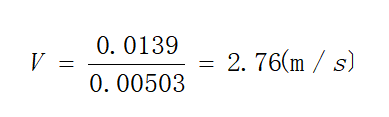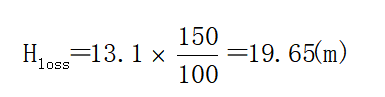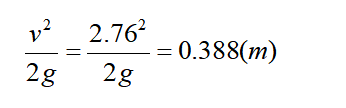1.Flow–Refers to the volume or weight of the liquid delivered by the water pump per unit time.Expressed by Q, the commonly used units of measurement are m3/h, m3/s or L/s, t/h.
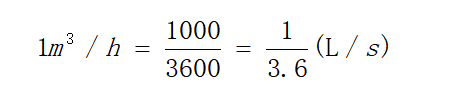 2.Head–It refers to the increased energy of transporting water with unit gravity from the inlet to the outlet of the water pump, that is, the energy obtained after the water with unit gravity passes through the water pump. Expressed by h, the unit is N.m/N, which is customarily expressed by the height of the liquid column where the liquid is pumped; Engineering is sometimes expressed by atmospheric pressure, and the legal unit is kPa or MPa.
2.Head–It refers to the increased energy of transporting water with unit gravity from the inlet to the outlet of the water pump, that is, the energy obtained after the water with unit gravity passes through the water pump. Expressed by h, the unit is N.m/N, which is customarily expressed by the height of the liquid column where the liquid is pumped; Engineering is sometimes expressed by atmospheric pressure, and the legal unit is kPa or MPa.
( Notes: Unit: m/p = ρ g h)
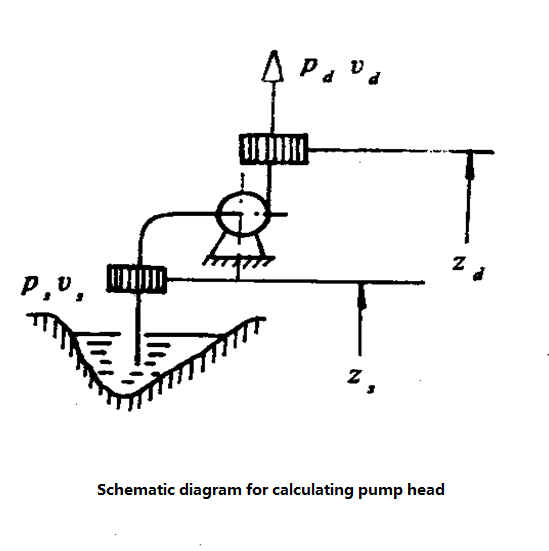
According to the definition:
H=Ed-Es
Ed-Energy per unit weight of liquid at the outlet flange of the water pump;
Es-Energy per unit weight of liquid at inlet flange of water pump.
Ed=Z d + P d/ ρg + V2d /2g
Es=Z s+ Ps / ρg+V2s /2g
Usually, the head on the nameplate of the pump should include the following two parts. One part is the measurable heading height, that is, the vertical height from the water surface of the inlet pool to the water surface of the outlet pool. Known as the actual head, part of it is the resistance loss along the way when water passes through the pipeline, so when choosing the pump head, it should be the sum of the actual head and the head loss, that is:
Example of pump head calculation
If you want to supply water to a high-rise building, suppose that the current water supply of the pump is 50m3/h, and the vertical height from the water surface of the intake pool to the highest delivery water level is 54m, the total length of the water delivery pipeline is 150m, the pipe diameter is Ф80mm, with one bottom valve, one gate valve and one non-return valve, and eight 900 bends with r/d = z, how large is the pump head to meet the requirements?
Solution:
From the introduction above, we know that the pump head is:
H = H real + H loss
Where: H is the vertical height from the water surface of the inlet tank to the highest conveying water level, that is : H real =54m
H loss is all kinds of losses in the pipeline, which are calculated as follows:
Known suction and drainage pipes, elbows, valves, non-return valves, bottom valves and other pipe diameters are 80mm, so its cross-sectional area is:
When the flow rate is 50 m3/h (0.0139 m3/s), the corresponding average flow rate is:
The resistance loss along the diameter H, according to the data, when the liquid flow rate is 2.76 m/s, the loss of 100-meter slightly rusted steel pipe is 13.1 m, which is the need of this water supply project.
The loss of drain pipe, elbow, valve, check valve and bottom valve is 2.65m.
Velocity head for discharging liquid from nozzle:
Therefore, the total head H of the pump is
H head = H real + H total loss = 54+19.65+2.65+0.388 = 76.692 (m)
When selecting high-rise water supply, the water supply pump with flow not less than 50m3/ h and head not less than 77 (m) should be selected.
Post time: Dec-27-2023